Security Risk Analysis: Designed For Healthcare
JUMP TO THE SECTION
- The Purpose of a Security Risk Analysis
- 5 Components of a Security Risk Analysis
- Is an SRA simply a one-and-done process?
- What is a security data breach within healthcare?
- Deadline: When must the SRA be completed?
- Critical HIPAA Requirements
- Administrative Safeguards
- Physical Safeguards
- Technical Safeguards
- SRA Compliance Resources
- How to Properly Conduct & Review a Security Risk Analysis
- Need Additional Assistance?
To conduct and review a Security Risk Analysis (SRA) is one of the most critical HIPAA requirements and Meaningful Use requirements you can accomplish for your organization. Every healthcare organization maintaining Protected Health Information (PHI) must be able to demonstrate the reasonable steps taken to analyze security risks to sensitive data. Here are the critical elements to know about completing an SRA for your organization before the end-of-year deadline.
The Purpose of a Security Risk Analysis
The purpose of an SRA is to identify protected health information (PHI) in all forms (physical and electronic) and assess any threats or vulnerabilities to that PHI. A thorough SRA must be completed each year to rule out the "what if" factors that could compromise your organization's security in a digital world (where security breaches are an increasing threat and compliance regulations are ever evolving).
5 Components of a Security Risk Analysis
- Examines all areas of the organization for analysis
- Identifies and assesses potential threats and vulnerabilities
- Implements an annually reviewed and updated corrective action plan
- Analyzes your personnel for exclusions and vulnerabilities
- Reviews your existing policies and procedures and examines their effectiveness.
For more information, check out these 5 best practices for performing an SRA.
Is an SRA simply a one-and-done process?
No, that's only a myth. The key is knowing an SRA is a continual process of improving your organization's policies and procedures addressing your patients' privacy and security with their protected health information (PHI). Learn more about top 5 myths and misconceptions about completing an SRA.
Risk analysis is an ongoing process for HIPAA-covered entities and business associates to:
- Periodically assess records and track access to ePHI
- Defend against and detect security incidents
- Evaluate the effectiveness of security measures
- Regularly re-evaluate potential risks to ePHI.
What is a security data breach within healthcare?
The statistics demonstrate the need for organizations to monitor and improve security measures.
The Statistics Landscape of U.S. Healthcare Data Breaches 2009 - 2021:
- Healthcare (15%) and finance (10%) are among the top targeted industries among malicious hackers: The loss of $25 billion dollars alone over two years is a must-know healthcare-sector cybersecurity stat for 2022. (Source: Verizon)
- Over 40 million records became exposed due to data breaches: Between March 2021 and February 2022, hackers remained busy with more than 1-in-10 of U.S. citizens and probably up to nothing good. (Source: HIPAA)
- 61% of data breach threats were traced back to negligent employees: Plus, consider 14% of data breaches caused by malicious activity or disgruntled staff helping a malevolent entity compromising a system or doing so on their own. (Source: Healthcare Innovation)
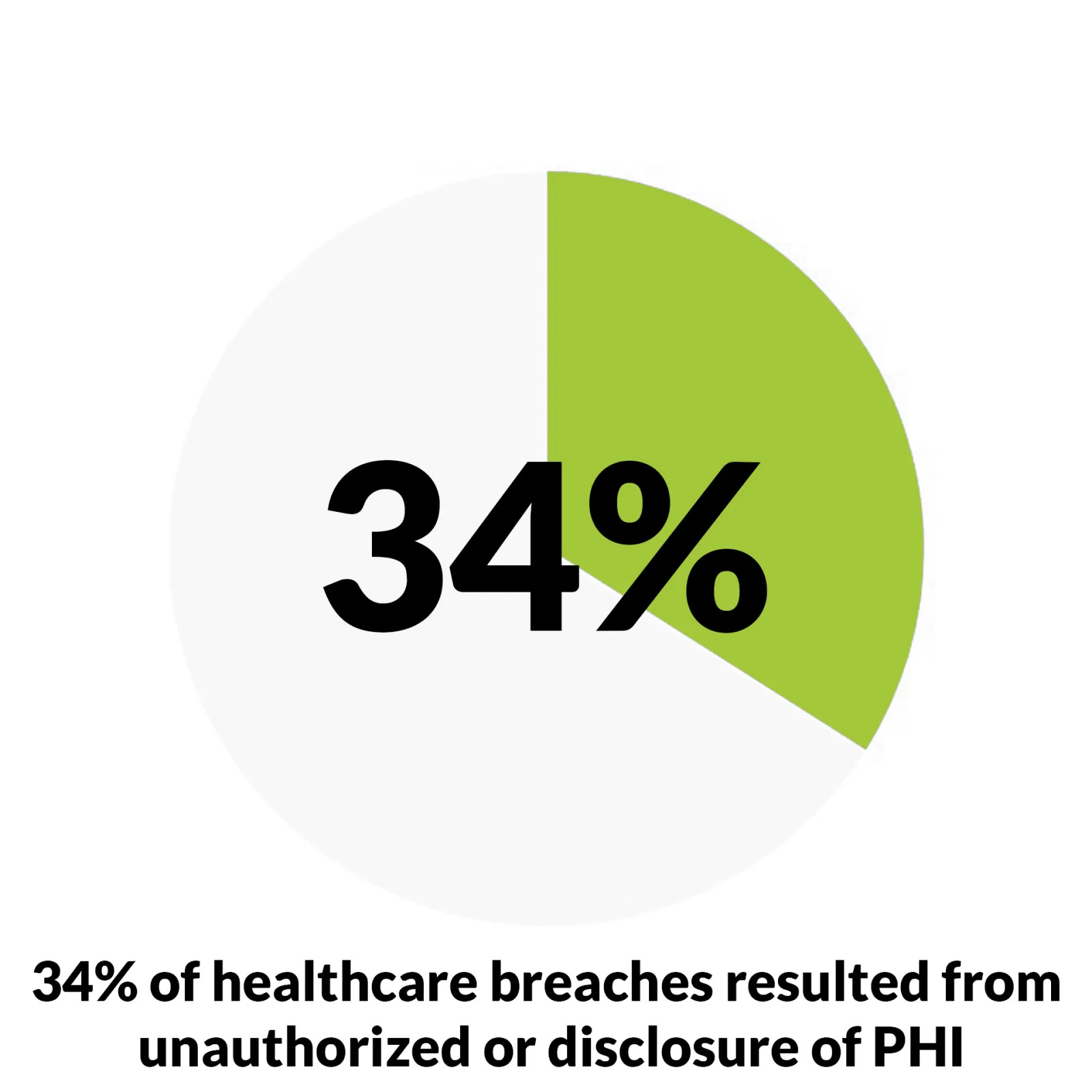
- 34% of healthcare data breaches resulted from unauthorized access or disclosure: The growth rate is shocking, up 162% over the last three years, so unauthorized access is a big deal. (Source: HHS OCR)
- 24% of physicians couldn't identify malware via common signs: The less awareness of how cyber attacks function, the more unable an organization will collectively be to identify, mitigate, and protect from risks (Source: Digital Guardian)
Deadline: When must the SRA be completed?
Healthcare organizations should conduct a Security Risk Analysis annually and, ideally, around the same time of year. For instance, we recommend every September of each calendar year as a best practice.
Organizations are advised not to complete their SRAs too close together. For example, even though dates can technically be considered as distinct calendar years, avoid conducting an SRA at the end of a calendar year in October and then conducting the next calendar year's SRA a few months later in February.
Sooner is better if your organization hasn't completed its SRA for the calendar year. The end of the year represents a reliably busy time for our compliance department to adequately review your SRA components and address those findings with you.
Critical HIPAA Requirements

The Security Rule requires covered entities and their business associates to conduct a risk assessment of their healthcare organization annually and provide an updated action plan each year. An SRA helps identify areas of compliance and areas of high risk that might need attention and improvement per HIPAA's physical, technical, and administrative safeguards.
Once an organization knows where its vulnerabilities are, an action plan can be developed to prepare for them, thus ruling out the "what if" factors. In addition to being a requirement under HIPAA, certain insurance policies (such as cybersecurity), credentialing bodies, or Quality Payment Programs may require a thorough SRA to be completed as part of their contract.
HIPAA-covered entities & business associates are required to comply with every Security Rule "Standard" and must implement policies and procedures to ensure the following safeguards: Administrative, Physical, and Technical Safeguards.
Administrative Safeguards
- Security Management Safeguards: A HIPAA covered entity must identify, mitigate, and protect against potential risks to ePHI and implement reasonable security measures that seek to reduce risks and vulnerabilities.
- Security Personnel: Designate a security official to be responsible for developing, implementing, and maintaining appropriate security policies and procedures.
- Information Access Management: Assess policies and procedures authorizing role-based access to ePHI, only when such access is valid due to the user's role and maintaining compliance with the Privacy Rule's standard to limit uses/disclosures of PHI to the "minimum necessary."
- Workforce Training and Management: Provide appropriate authorization and supervision of workforce members working with e-PHI. Furthermore, your organization must provide workforce training to all your members regarding its security policies and procedures, including appropriate sanctions against workforce members found in violation.
- Evaluation: Perform a periodic assessment to determine the effectiveness of security policies and procedures for meeting the Security Rule requirements.
Physical Safeguards
- Facility Access and Control: Require limits on physical access to facilities while providing authorized access too.
- Workstation and Device Security: Specify the proper use/access to digital workstations and electronic media formats. In addition, specify the appropriate types of transfer, removal, disposal, and re-use of electronic media in a way that protects ePHI.
- Technical Safeguards Access Control: The goal is to only allow personnel who possess authorized access to electronic protected health information.
- Audit Controls: Implement hardware, software, and/or procedural mechanisms that record and examine access activity within information systems of e-PHI.
- Integrity Controls: Ensure the electronic measures to confirm that e-PHI has not been improperly altered or destroyed.
- Transmission Security: Guard against unauthorized access to e-PHI that is being transmitted over an electronic network.
Technical Safeguards
- Access Control: Implement technical policies and procedures enable authorized personnel only to access ePHI.
- Audit Controls: Install hardware, software, and/or procedural mechanisms to record/examine access and user activity within information systems containing or using ePHI.
- Integrity Controls: Ensure policies and procedures so ePHI will never be improperly altered or destroyed.
- Transmission Security: Guard against unauthorized access to ePHI via electronic network transmissions.

SRA Compliance Resources
How to Properly Conduct & Review a Security Risk Analysis
Fulfill your HIPAA requirements with a SRA tool designed to identify risk areas to address and implement the safeguard-compliant policies and procedures for a digital world. Healthcare Compliance Pros provides an online Security Risk Analysis as a resource for you and your organization.
Upon submission of your SRA, you will have access to our HIPAA Security experts who will provide a comprehensive review and create an action plan to identify any gaps and document specific remedies for each threat. Fill out what areas were addressed or corrected and the result gives demonstrated proof of your organization's ongoing compliance efforts to analyze the security risks around sensitive data.
Need Additional Assistance?
HCP can provide on-site visits to perform an SRA, a HIPAA Walkthrough, and other critical assessments to maintain compliance.
Luckily, our SRA is designed to act as 'living and breathing' documentation for previous information your healthcare organization entered before, so you won't have to start an SRA from scratch each year. Our clients can save SRA reports marked as completed, archived, and access later as you need via login into the HCP Portal or contact your team of dedicated compliance advisors for more information.
If you are not an HCP client yet, schedule a free online consultation to learn how you can simplify compliance. Be sure to ask our client services team about getting a security risk analysis prepared for your organization.

